Xiaofeng Wang Research Program
-
Xiaofeng Wang Research Program
- Principal Investigator
- Research
- Our Team
- Publications
- Careers
- Research News
Research
Dr. Wang's primary research areas include Clinical Prediction Modeling, Radiomics, Causal Machine Learning with Real-World Data, Clinical Informatics, and Bayesian Inference. He has developed innovative statistical models and machine learning algorithms to address complex data science challenges in medicine—particularly those involving large-scale electronic health records (EHRs) and medical imaging. His clinical application areas span Pulmonary Medicine, Critical Care Medicine, Infectious Diseases, Neurological Diseases, Cardiovascular Diseases, and more. As part of his collaborative efforts, his team has developed a suite of software tools, including advanced analytics pipelines, EHR data engineering frameworks, platforms for multi-site data integration and mining, and online risk prediction tools.
Biography
Xiaofeng Wang, Ph.D., is a Full Staff Member in the Department of Quantitative Health Sciences at Cleveland Clinic and a Professor of Medicine at the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University. He serves as Co-Head of the Section of Data Science, Artificial Intelligence, and Statistics at the Cleveland Clinic Integrated Hospital-Care Institute. He also holds a joint faculty appointment in the Department of Population and Quantitative Health Sciences at the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine.
Dr. Wang has authored over 200 journal articles in the statistical and medical literature, as well as numerous book chapters and conference proceedings. He currently serves as a Statistical Editor for Chest and as a member of the Statistical Advisory Board for Nature Medicine. He is an Elected Fellow of the American Statistical Association (ASA) and an Elected Member of the International Statistical Institute (ISI).
Education & Professional Highlights
Education
Ph.D. in Statistics, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, USA, 2005.
Honors and Awards
- Elected Fellow of the American Statistical Association (ASA)
- Elected Member of the International Statistical Institute (ISI)
- Cleveland Clinic Innovator Award, 2010
- Researcher Selected for the 2006-7 The Value of Research, Case Western Reserve University
Professional Society Affiliations
- American Statistical Association
- Institute of Mathematical Statistics
- International Statistical Institute
"CIMER Trained Mentor" indicates the principal investigator has completed mentorship training based on curriculum from the Center for the Improvement of Mentored Experiences in Research, aimed at advancing mentoring relationships and promoting cultural change in research.
Research
Overview
The Clinical Machine Learning Lab is interested in developing novel machine learning and artificial intelligence methods and using these techniques to advance health care. Our current on-going research projects include:
- Causal Machine Learning with Real‐World Data

Our research involves developing novel machine learning methodologies to advance causal inference in clinical research. We focus on developing algorithms for causal clustering and refining models to accurately predict heterogeneous treatment effects. Through these advancements, we develop robust modeling frameworks with target trial emulations that effectively leverage real-world evidence (RWE). Our methodologies drive innovations across COVID-19, critical care, and cardiovascular and lung diseases, ultimately improving patient outcomes and informing clinical decision-making.
- Radiomics
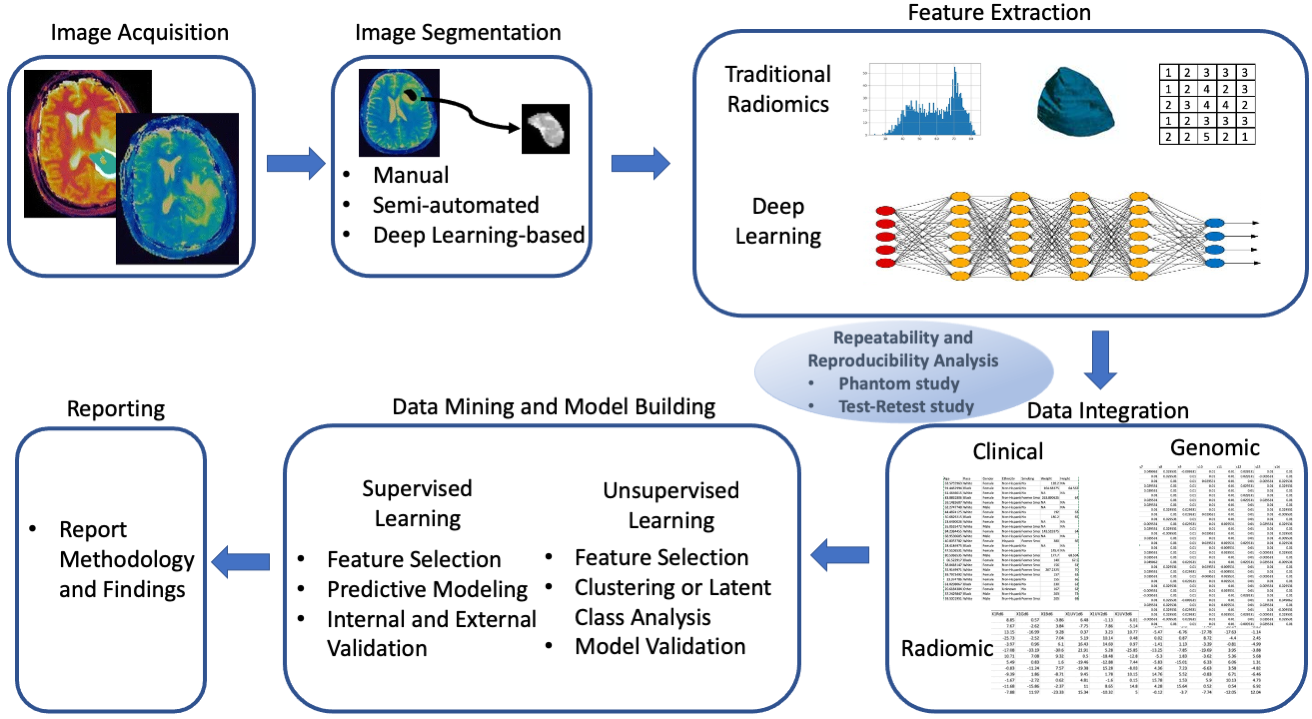
Radiomics involves extracting high-dimensional quantitative features from medical images, which are then analyzed using machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and make clinical predictions. We develop various radiomics models aimed at enhancing their quality and clinical utility across multiple medical fields.
- Modeling with MR Fingerprinting in Cardiovascular and Brain Research
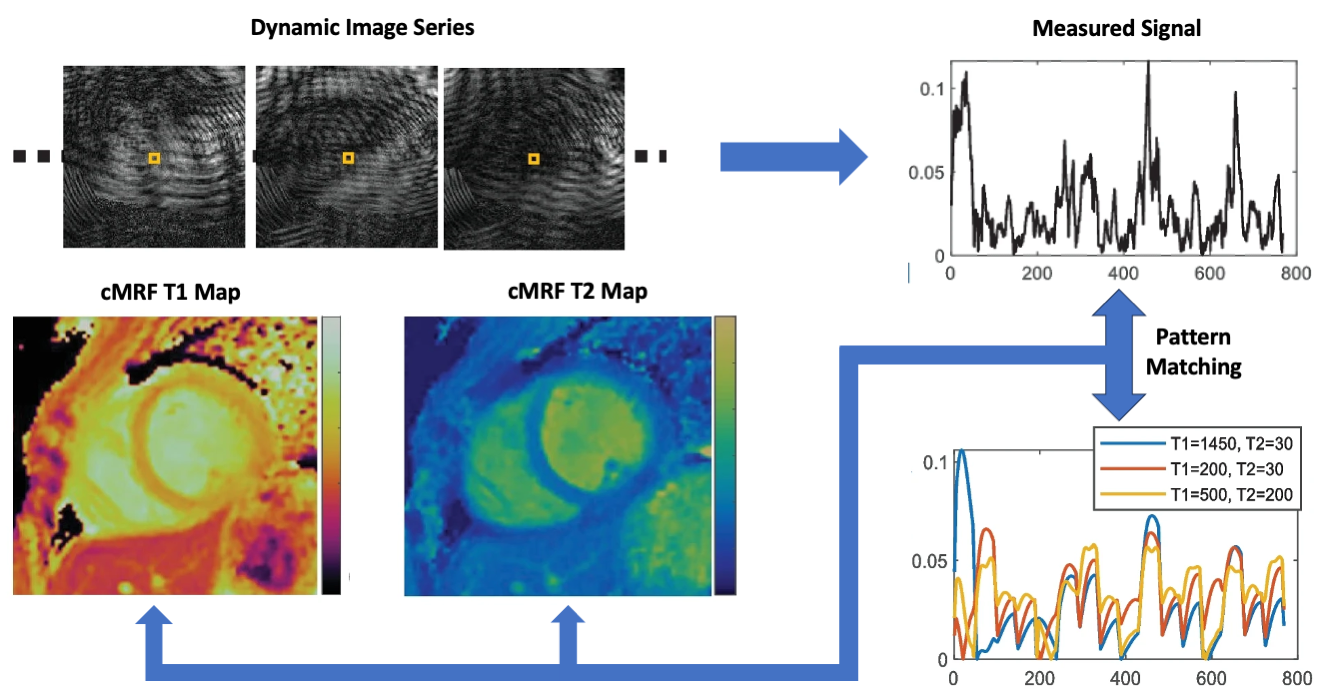
We use the novel Magnetic resonance fingerprinting (MRF) technique to generate high-resolution quantitative tissue property maps (T1 and T2 maps), and develop machine learning and artificial intelligence prediction models in areas of Cardiovascular and Brain Research.
Announcements
30 June, 2023
The Department of Quantitative Health Sciences (QHS) is pleased to announce that Xiaofeng Wang, PhD, has been elected as a 2023 Fellow of the American Statistical Association (ASA).
The ASA is the world’s largest community of statisticians and is the second-oldest continuously operating professional association in the country. The designation of ASA Fellow has been a significant honor for over 100 years. Under ASA bylaws, only one-third of one percent of the total association membership may be elected as fellows each year. Fellows are evaluated on their contributions to the advancement of statistical science, the impact of their published works, their position with their employer and activities with the ASA and other professional societies. “To be honored, nominees must have an established reputation in the profession and have made outstanding contributions to statistical science,” the ASA says.
Dr. Wang's citation by the Committee on Fellows reads, “for outstanding scholarly contributions to the methods and applications in the areas of quantitative imaging analysis, clinical data modeling, and approximate Bayesian inference; for significant contributions to collaborative research in medicine”.
Our Team
Selected Publications
Peer Reviewed Books
Wang, X.F., Yue, Y.R., and Faraway, J. (2018). Bayesian Regression Modeling with INLA. Chapman & Hall/CRC Computer Science and Data Analysis Series.
Peer Reviewed Article
(over 200 peer-reviewed papers)
Lin, D.-Y., Huang, S., Milinovich, A., Duggal, A., Wang, X.F. (2024). Effectiveness of XBB.1.5 vaccines and antiviral drugs against severe outcomes of omicron infection in the USA. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00150-6.
Lin, D.-Y., Abi Fadel, F., Huang, S., Milinovich, A.T., Sacha, G.L., Bartley, P., Duggal, A. and Wang, X.F. (2023). Nirmatrelvir or Molnupiravir Use and Severe Outcomes From Omicron Infections. JAMA Network Open, 6(9), e2335077.
Wang, X.F., Pennello, G., DeSouza, N.M., Huang, E.P., Buckler, A.J., Barnhart, H.X., Delfino, J.G., Raunig, D.L., Wang, L. , Guimaraes, A.R., Hall, T.J., Obuchowski, N.A. (2023). Multiparametric Data-driven Imaging Markers: Guidelines for Development, Application and Reporting of Model Outputs in Radiomics. Academic Radiology, 30(2): 215-229.
Wang, X.F., Zein, J., Ji, X. and Lin, D.-Y. (2023). Impact of Vaccination, Prior Infection and Therapy on Omicron Infection and Mortality. Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac460.
Ren, R., Fang, K., Zhang, Q., and Wang. X.F. (2023) Multivariate Functional Data Clustering Using Adaptive Density Peak Detection. Statistics in Medicine, 1-18, doi:10.1002/sim.9687.
Sun, Y., Li, J., Xu, Y., Zhang, T., & Wang, X. (2023). Deep learning versus conventional methods for missing data imputation: A review and comparative study. Expert Systems with Applications, 120201.
Wang, Y., Yan, G., Wang, X.F., Li, S., Peng, L., Tudorascu, D.L., and Zhang, T. (2023). A Variational Bayesian Approach to Identifying Whole-Brain Directional Networks with fMRI Data. The Annals of Applied Statistics. 17(1), 518-538.
Sun, H. and Wang, X.F. (2022). High‐dimensional feature selection in competing risks modeling: A stable approach using a split‐and‐merge ensemble algorithm. Biometrical Journal. doi.org/10.1002/bimj.202100164.
Yue, Y., Bolin, D., Rue, H., and Wang, X.F. (2019). Bayesian Generalized Two-way ANOVA Modeling for Functional Data Using INLA. Statistica Sinica, in press.
Wang, X.F. and Xu, Y. (2017) Fast clustering using adaptive density peak detection. Statistical Methods in Medical Research, 26(6), 2800-2811.
Yue, Y.R. and Wang, X.F. (2016). Bayesian inference for generalized linear mixed models with multiple predictors subject to detection limits. Statistics in Medicine, 35(10):1689-705.
Faraway, J., Mahabal, A., Sun, J., Wang, X.F., Wang, Y., Zhang, L. (2016) Modeling light curves for improved classification of astronomical objects. Statistical Analysis and Data Mining. 9(1), 1-11.
Wang, X.F., and Ye, D. (2015). Conditional density estimation in measurement error problems. Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 133:38-50.
Sattar, A., Sinha, S.K., Wang, X.F. and Li, Y. (2015). Frailty models for pneumonia to death with a left-censored covariate, Statistics in Medicine. 34(14):2266-2280.
Huang E.P., Wang X.F., Roy Choudhury K, McShane L.M., Gönen M., Ye J., Buckler A.J., Kinahan P.E., Reeves A.P., Jackson E.F., Guimaraes A.R., Zahlmann G. (2015). Meta-analysis of the technical performance of an imaging procedure: Guidelines and statistical methodology. Statistical Methods in Medical Research. 24(1):141-74.
Mazzone, P., Wang, X.F., Xu, Y., Mekhail, T., Beukemann, M.C. Na, J., Kemling, J.W., Suslick, K.S., Sasidhar, M. (2012). Exhaled breath analysis with a colorimetric sensor array for the identification and characterization of lung cancer. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 7(1): 137-142.
Wang, X.F., Jiang, Z., Daly, J.J. and Yue, G.H. (2012). A generalized regression model for region of interest analysis of fMRI data. NeuroImage, 59(1), 502-510.
Wang, X.F. and Wang, B. (2011). Deconvolution estimation in measurement error models: The R package decon. Journal of Statistical Software, 39(10), 1-24.
Careers
Training at Lerner Research Institute
Our education and training programs offer hands-on experience at one of the nationʼs top hospitals. Travel, publish in high impact journals and collaborate with investigators to solve real-world biomedical research questions.
Learn MoreResearch News

Investigators are developing a deep learning model to predict health outcomes in ICUs.

The Cleveland Clinic study provides clinical evidence supporting the use of the modern vaccine against Omicron sub-variants.

Observational study analyzed nearly 70,000 patients diagnosed with the disease at Cleveland Clinic.

Dr. Wang is recognized for his contributions to machine learning and healthcare analytics.
